23rd-November-2022 | ZebPay Trade-Desk
The Blockchain technology is the core and basis of Bitcoin (BTC) and many other crypto assets. The Bitcoin network is made up of blocks that are interdependent. Together these blocks form the blockchain. Blocks are similar to files that contain information about the latest transactions made on the network. Smaller blocks require less processing resources for validation (or vice versa) because they behave like data files. Hashing comes into play in this situation. Confirming the integrity of network transactions is known as “hashing” a block, and network participants receive BTC or hash as a reward. So what does hash rate mean for miners and crypto investors?
What is Hash Rate?
A hash rate, which can be expressed in billions, trillions, quadrillions, and quintillions, is a measure of how many calculations can be performed per second. For example, a hash rate of 1BH/s indicates that 1 billion guesses can be made per second. But how is Bitcoin hashrate measured? Exa Hashes per second (EH/s), which equals one trillion hashes, is used to express BTC hashrate. By comparing the average time between mined blocks with the difficulty of the network at any given point in time, the hash rate of the entire network can be roughly calculated.
So what is the mining difficulty? Mining challenge refers to how difficult it is for miners to generate a hash lower than the desired hash, which is achieved by reducing the numeric value of the hash block header. On average, a new block (Bitcoin) is formed every ten minutes. However, if BTC is discovered less often than the average time, the difficulty decreases or vice versa.
Read more: What is Bitcoin Mining
In addition, it is important to note that the Bitcoin network’s mining difficulty changes automatically after Bitcoins are mined. So, based on the number of miners and their total hash power in the mining network, the difficulty can be adjusted up or down.
Importance of Hash Rate
Calculating a hash rate could help individual miners predict their profitability. However, since crypto assets are mined using different types of mining equipment, the hash rate of each machine is different. Because mining requires different levels of processing speed, memory, and performance, the network hash rate increases as mining equipment is upgraded or vice versa. However, since the network is designed to release a certain amount of Bitcoin at a time, a more robust network does not necessarily result in faster BTC withdrawals.
The number of miners on the network, the difficulty of mining, and ultimately miner profitability are all affected by changes in hash power. Also, the challenge of mining increases as more miners join the network, as it takes more guesses per second to solve the complex mathematical equation and get a reward of blocks. As a result, when the difficulty of the Bitcoin network increases, the hash rate increases. Likewise, for crypto investors, the hash rate is a crucial indicator of how secure a crypto’s Proof of Work (PoW) network can be against hackers. Network attacks become more expensive and difficult as the hash rate increases
Process Flow of Mining
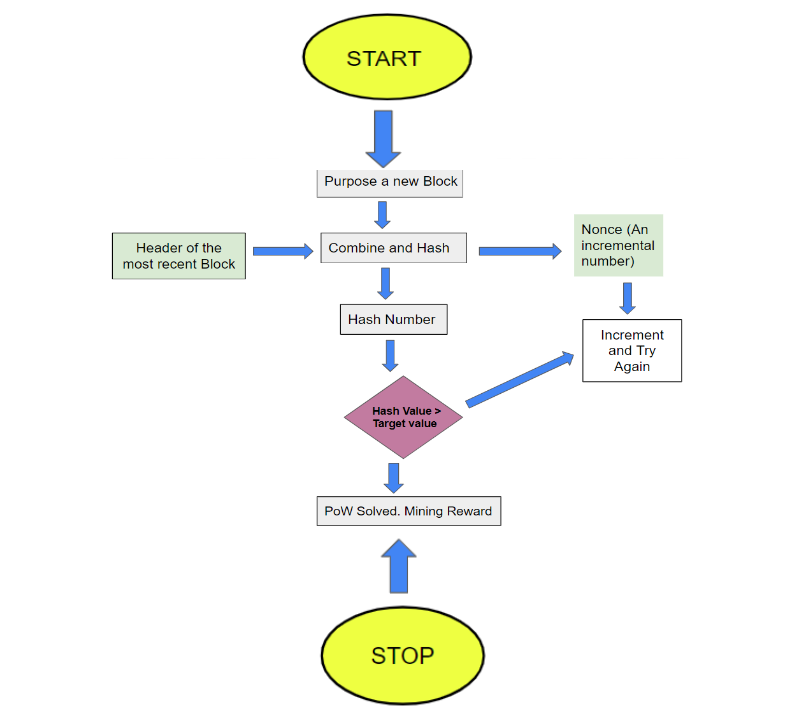
So, what takes place if Bitcoin’s hash charge increases? The hash charge rises as extra machines are dedicated for mining to locate the subsequent block, signifying that the community’s general computational electricity is increasing and it’s tough for malicious actors to intervene with the community. Nonetheless, the bulk hash rate controller can override and go backward by re-organizing bills, causing double-spending issues because of a fall within the community’s hash rate.
Now, what takes place if Bitcoin’s hash charge decreases? A decrease in hash charge exposes the community to cyber criminals and crypto heists because of the low value of executing a 51% attack. In addition, a decreased hash charge makes crypto much less decentralized, posing a big hazard to crypto investors. To guard its customers towards dropping funds, crypto platforms ought to prevent buying and selling or delisting a crypto if the hash charge all at once drops.
So, Is a large hash charge a good indicator of a community’s protection?
A larger hash charge is ideal for the general protection and balance of the blockchain community because it requires extra costs, extra miners and extra time for the blockchain to be taken down.
So What is the Current Hash Rate of Bitcoin?
Although the exact hash power of Bitcoin is unknown, it can be inferred from the number of blocks currently being mined and the difficulty of the blocks. Blockchain.com provides estimates of the current hash rate of Bitcoin which is 231.44 million TH/s as of November 23, 2022.
Conclusion
The more computing power the Bitcoin network uses, the greater its value. Furthermore, rational miners are only willing to mine BTC if it is profitable, which implicitly means that without demand any crypto would be worth zero and miners would divert their resources elsewhere. This premise is explicitly backed by the algorithm driving the Bitcoin network, meaning that the difficulty will be readjusted to offset the drop or, if not, mitigate the impact of increasing mining power.
Fluctuations in the price of bitcoin matters not only for deciding to buy or sell but also because of how it affects the power consumption of the bitcoin network and how the miners running the bitcoin infrastructure will behave in the future. Additionally, it has long been believed that the hash rate, or the total number of calculations performed by Bitcoin miners, and the price of BTC are related.
However, this notion may seem wrong since a manufacturer’s effort to produce a good or service is disproportionate to the price paid by consumers as producers are price takers in competitive markets. Conversely, this may not apply to the Bitcoin market as there are few mining pool operators who coordinate their operations to control the market price. Additionally, the inelasticity of bitcoin supply and intense competition in the mining industry could prompt miners to act differently.
Disclaimer : This report is not intended to be relied upon as advice to investors or potential investors and does not take into account the investment objectives, financial situation or needs of any investor. All investors should consider such factors in consultation with a professional advisor of their choosing when deciding if an investment is appropriate. The Company has prepared this report based on information available to it, including information derived from public sources that have not been independently verified. No representation or warranty, express or implied, is provided in relation to the fairness, accuracy, correctness, completeness or reliability of the information, opinions or conclusions expressed herein. This report is preliminary and subject to change; the Company undertakes no obligation to update or revise the reports to reflect events or circumstances that arise after the date made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. Trading & Investments in crypto assets viz. Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum etc.are very speculative and are subject to market risks. The analysis by Author is for informational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice.

