Ripple operates on an open-source, decentralized peer-to-peer infrastructure that enables the seamless transfer of various forms of currency, including both fiat and crypto assets. In this system, financial institutions like governments, banks, and investment firms hold centralized authority over the flow of money and related activities. This applies to traditional financial services and forms a global payment network with major banks as its clients. Ripple’s native token, XRP, is used to facilitate the exchange of different crypto assets.
Centralized finance (CeFi) refers to a financial ecosystem where a central authority manages financial assets and services, while users access and utilize these services. This authority can be exercised by an individual, group, or organization. The key advantage of CeFi is its ability to offer greater stability and security for investors, as it typically requires users to verify their identities before using platforms like centralized exchanges.
Ripple: A Brief Overview
Ryan Fugger started RipplePay in 2004. Users could use it to provide credit to others. Jed McCaleb began working on the XRP blockchain in 2011. In 2012, he assembled a team, found investors, and approached Fugger about using his RipplePay network, who agreed to hand over control of RipplePay. They launched the XRP blockchain in 2012. It was initially known as NewCoin before being renamed OpenCoin and eventually Ripple. The XRP Ledger records all transactions issued in a given currency by each user. All credits and transactions are publicly viewable on the XRP ledger.
Ripple uses HashTree as its consensus mechanism. The difference between this system and a Proof-of-Work (PoW) system is that consensus is reached by comparing only a single value derived from summarizing the ledger’s data. Individuals, banks, and institutions run these independent validation servers. Its validating system is run by individuals or organizations, such as banks. The Ripple network uses drops as a unit of measurement for XRP transactions, making them inexpensive and accessible. Ripple can handle large transactions per second, making it an attractive alternative for fintech companies that need robust infrastructure and a crypto payment gateway.
Read more: What is Ripple (XRP)
Centralized Finance (CeFi) and its Components
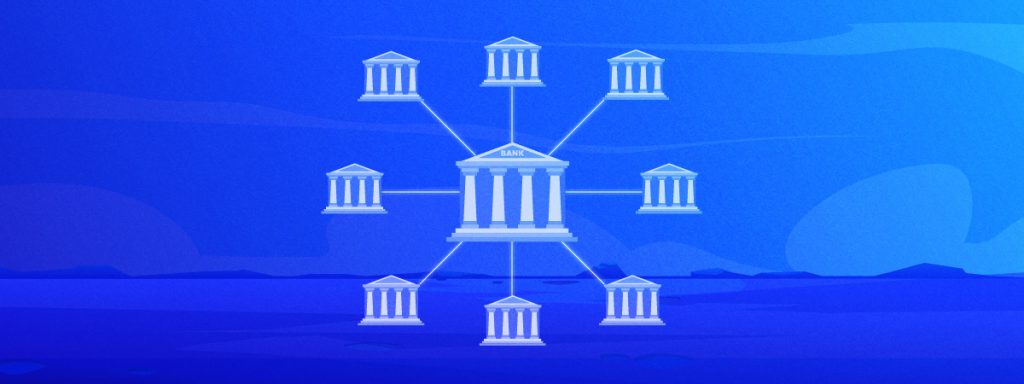
Centralized finance is a financial activity in which investors can earn interest and acquire loans on their crypto holdings through centralized exchanges. Private keys to crypto assets would be handed to the desired third-party company to carry out crypto transactions. It aims to improve the performance and cost-efficiency of crypto transactions. It combines the yield services of decentralized finance (DeFi) with the reliability of conventional financial services to enable crypto lending, purchasing, and trading. Some essential CeFi components include centralized exchanges (CEXs), higher interest rates, and fiat conversion flexibility.
A centralized exchange is a platform owned and maintained by a single business that serves as a middleman between buyers and sellers. This intermediary facilitates transactions by providing liquidity for supported tokens. It uses an order book system to set crypto prices same as traditional institutions like banks. Users deposit funds into an account kept by the exchange, which acts as a custodian of the funds. Centralized finance (CeFi) protocols set their interest rates, which makes them comparatively more stable, but these rates are much higher than DeFi protocols. Centralized entities offer more adaptability for converting crypto to fiat and vice versa. Usually, trading cryptos for money necessitates the intervention of a centralized entity; however, DeFi solutions do not do so.
Read more: DeFi vs CeFi
Advantages and Limitations of Ripple in CeFi
Advantages
- Fast settlement: Transaction confirmation speeds are fast in the Ripple network. It takes about four to five seconds to complete a transaction in Ripple compared to days in CeFi institutions.
- Low fees: The cost to complete one transaction in Ripple is just 0.0001 XRP.
- Versatile network: Apart from XRP, Ripple can also process transactions in other fiat currencies and crypto.
Limitations
- Centralized: Ripple is partially centralized as it has a list of its validators, which goes against the principle of decentralization.
- Large pre-mined XRP: Most Ripple token supplies are not in circulation but stored in escrow, and large amounts of tokens can be introduced at any given time, affecting the price of the token.
The Impact of Ripple XRP on CeFi and DeFi
Ripple offers a versatile platform where any currency or crypto asset can be used for transactions, though XRP plays a crucial role as a bridge between currencies when liquidity is needed. By leveraging RippleNet, there’s no need for pre-funded accounts, as it provides on-demand liquidity. Ripple has formed strong partnerships with leading financial institutions like Bank of America, Santander, and American Express, enabling seamless and efficient cross-border transactions.
XRP can be used just like other digital assets, whether for transactions or investment purposes. Ripple’s network also facilitates various types of transactions, such as currency exchanges, with greater ease.
For instance, if you want to convert INR to USD, you can exchange INR for XRP and then use it to buy USD, rather than relying on traditional bank or exchange conversions. This method is often faster and more cost-effective, bypassing the high fees typically charged by money transfer companies. XRP’s key function is to act as a bridge asset, helping financial institutions convert between fiat and crypto assets quickly and at a low cost.
Read more: Ripple Price Prediction
Unravel everything that you need for your crypto journey via ZebPay blogs. Get started today and join 6 million+ registered users on ZebPay!