Decentralized Finance (DeFi) marks a transformative shift in how we manage money, using blockchain technology to recreate traditional financial systems in a fully open, transparent, and permissionless environment. By eliminating intermediaries like banks and brokers, DeFi enables users to lend, borrow, trade, and earn interest directly through peer-to-peer networks. Leveraging blockchain’s key strengths—immutability, transparency, and decentralization—it relies on smart contracts to execute transactions without needing trusted institutions. Beyond streamlining processes, DeFi enhances financial inclusion, reduces operational costs, and gives individuals greater control over their assets, all while offering privacy and global accessibility.
How can DeFi Address the Limitations of the Current Financial System?
DeFi runs on peer-to-peer financial networks, blending blockchain technology with secure protocols and modern connectivity to remove intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. In conventional systems, these middlemen are required to process transactions, often incurring high fees. DeFi challenges this model by leveraging smart contracts to automate activities like lending, borrowing, and trading directly between users. This decentralized setup boosts transparency and efficiency while lowering transaction costs, making financial services more accessible and affordable for people around the globe.
Benefits of Decentralised Finance
DeFi provides the following benefits:
- Accessibility: With just an internet connection, users can access DeFi platforms without geographical limitations.
- Affordable and High-Interest Transactions: DeFi facilitates direct negotiation of interest rates between parties, allowing for low-cost crypto or fiat money lending via DeFi networks, with attractive interest rates.
- Security and Transparency: DeFi platforms leverage blockchain technology, offering smart contract transparency and immutable records of transactions. This ensures security and accountability without revealing user identities.
- Autonomy: DeFi networks operate independently of centralised financial institutions, reducing administration costs and enhancing financial service efficiency.
Read more: How to Invest in DeFi
Use Cases of DeFi
Users typically interact with DeFi through decentralised applications (dApps), many of which are currently operational on the Ethereum blockchain. Here are some common ways individuals engage with DeFi today:
- Lending: Earn interest and rewards continuously by lending out your crypto.
- Borrowing: Access instant loans without extensive paperwork, including short-term “flash loans” not typically offered by traditional financial institutions.
- Trading: Engage in peer-to-peer trading of specific crypto assets, similar to buying and selling stocks without requiring a brokerage.
- Saving: Deposit crypto into alternative savings accounts to earn higher interest rates than those offered by banks.
- Derivatives Trading: Speculate on asset prices with long or short positions, akin to stock options or futures contracts in the traditional financial markets.
Decentralised Lending and Borrowing Platforms
Following are some examples of Lending and Borrowing DeFi platforms:
Aave (AAVE)
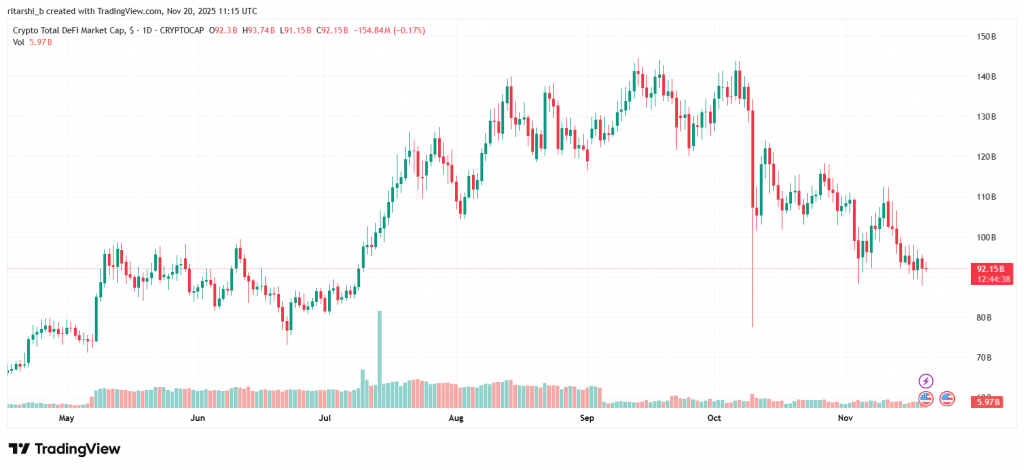
Aave, operating on the Ethereum blockchain, is a DeFi protocol providing diverse decentralized lending services. Users can engage in lending, borrowing, and earning interest on various digital assets or crypto assets. Similar to traditional financial lending, Aave requires borrowers to provide collateral or have collateral delegated to access crypto loans.
At the time of writing, AAVE was trading at around $176.88, having a market capitalization of around $2.70 billion.
Read more: What is Aave (AAVE)
Compound (COMP)
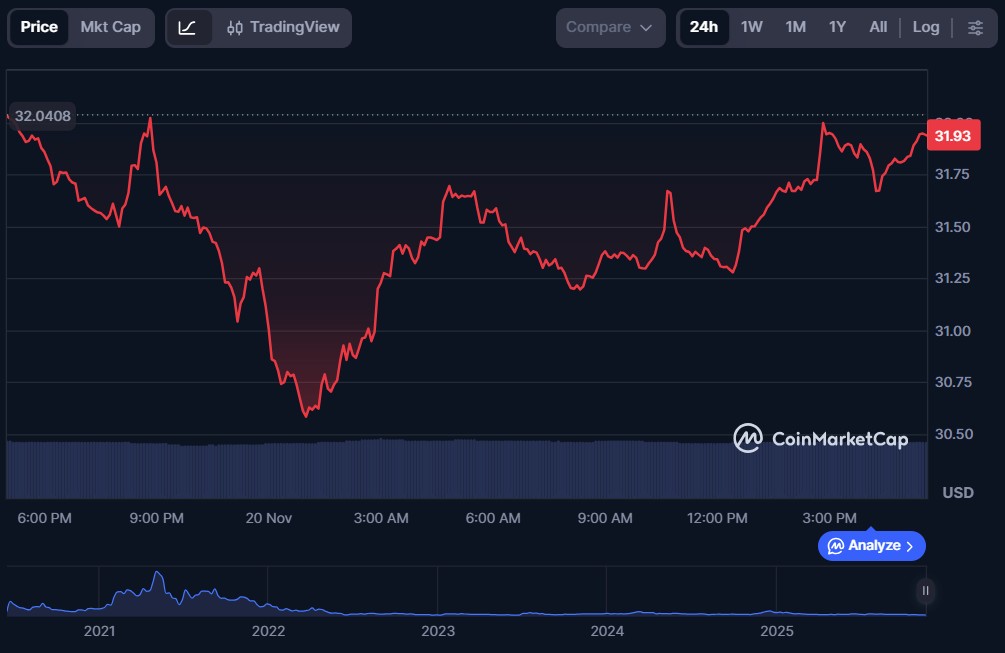
Compound Finance, like Aave, enables users to quickly lend or borrow crypto assets within minutes. The platform’s smart contracts, which form the algorithmic money market protocol, streamline the process for users, automatically determining collateral requirements and interest rates without the need for direct negotiation between borrowers and lenders.
As of now, COMP is trading near $31.90, with a total market capitalization of approximately $307.86 million.
Read more: How Does DeFi Lending Work
Stablecoins and Their Usage in DeFi Applications
Stablecoins are crypto assets pegged to match a financial asset or currency like the US Dollar or gold. True to their name, the values of these tokens are relatively stable. These are very popular among crypto traders who want a non-volatile store of value:
Dai (DAI)
Dai, a widely recognised USD-pegged stablecoin, is overseen by Maker and its decentralised governance community, MakerDAO. Dai maintains its value in line with the US dollar through collateral deposits from users, which in turn generates Dai’s supply. For instance, when a user deposits Ether as collateral into a Maker Vault to generate Dai, they can utilise it in other DeFi protocols or decentralised applications.
At the time of writing, DAI was valued at approximately $1, with a total market capitalization of about $5.36 billion.
Read more: What Is DAI
Tether (USDT)
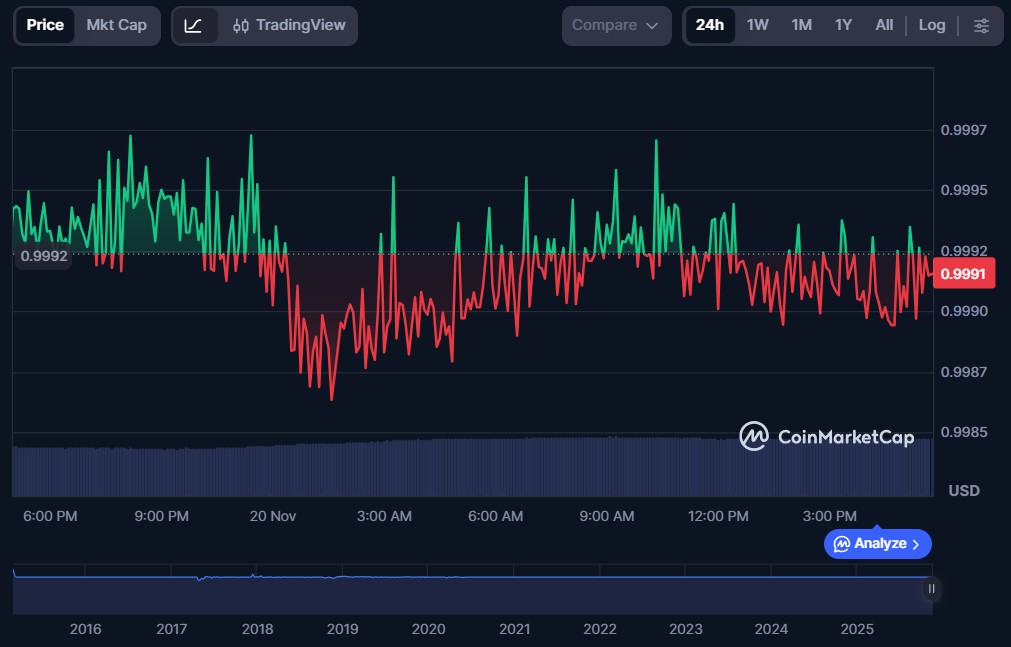
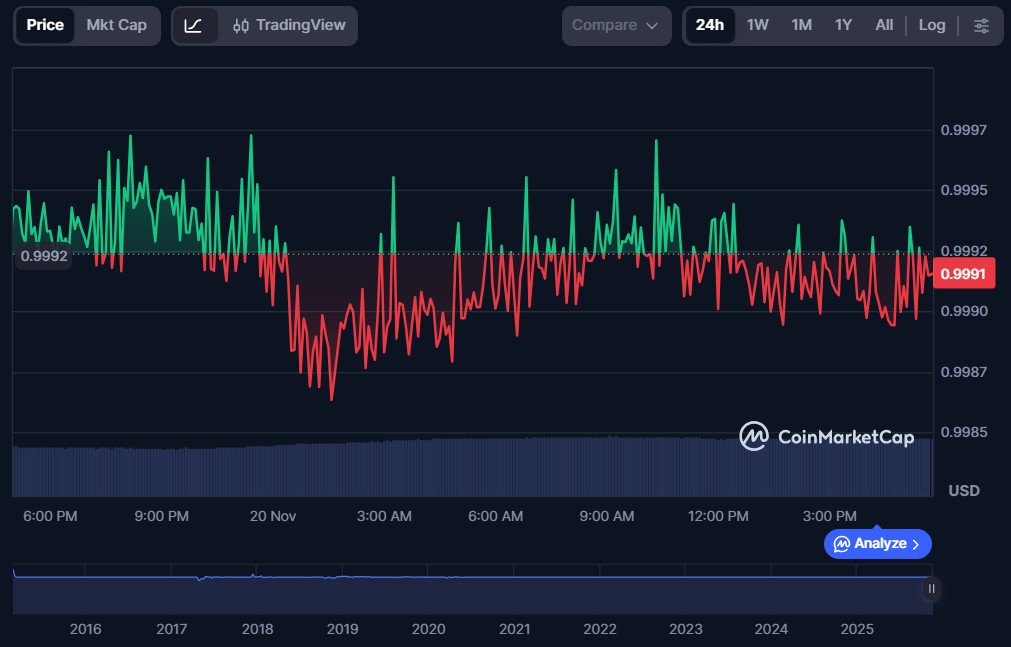
USDT, one of the oldest and most widely used stablecoins, is issued by Tether Limited. It maintains its 1:1 peg to the US dollar by holding a mix of cash reserves, short-term deposits, and other liquid assets. For example, when an exchange or user deposits USD with Tether, an equivalent amount of USDT is issued, allowing them to trade or transfer funds across exchanges instantly without relying on traditional banking channels.
At the time of writing, USDT was trading near $0.9991, with a market capitalization of roughly $183.73 billion.
USD Coin (USDC)
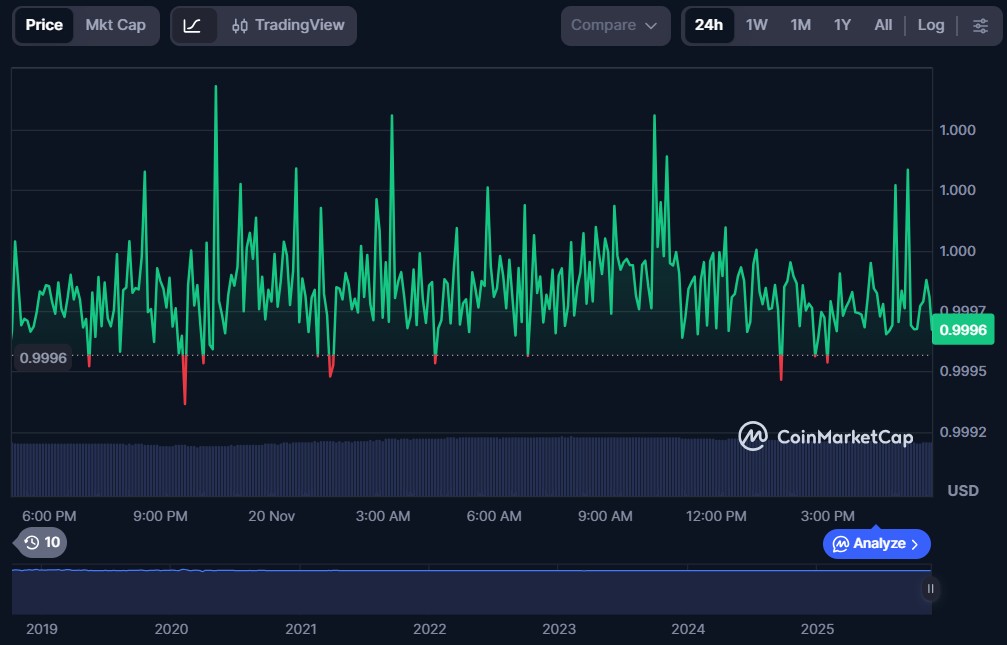
USDC, managed by Circle and governed by the Centre Consortium (which includes Coinbase), is a fully collateralized stablecoin backed by cash and short-term U.S. Treasuries. Its transparency and regular audits have made it a preferred choice among institutional and retail users. For instance, when a user transfers $1 to Circle, they receive 1 USDC in return, which can then be used across DeFi platforms, exchanges, or payment applications with full on-chain traceability.
At the time of writing, USDC was valued at around $0.9996, with an estimated market capitalization of $74.37 billion.
Future of DeFi
The future of crypto holds immense potential for transformation. Market projections indicate that the total value of digital assets could triple by 2030, driven by growing adoption and clearer regulatory frameworks worldwide. As governments increasingly recognize the benefits of crypto assets, opportunities across industries are set to expand. Ongoing technological advancements—ranging from improved blockchain scalability and interoperability to enhanced DeFi infrastructure—will continue to propel this growth. Collectively, these developments are positioning crypto to evolve from a niche investment arena into a fully integrated cornerstone of the global financial system.
Read more: What Is The Future Of Decentralised Finance
Conclusion
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) revolutionises traditional financial systems by leveraging blockchain technology to offer accessibility, affordability, security, autonomy, and innovative financial services. Through DeFi platforms, users can engage in lending, borrowing, and trading with ease, while stablecoins provide stability and utility within the DeFi ecosystem.
The future of DeFi looks promising and the community is actively building more innovative products. New support from the community as well as governments and regulators are expected. This can potentially transform the way we interact with financial services.
Unravel everything that you need for your crypto journey via ZebPay blogs. Get started today and join 6 million+ registered users on ZebPay!