History of Ethereum
Why was Ethereum created?
Ethereum is a decentralised, open-source blockchain platform that was first proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a programmer and crypto researcher. The project was officially launched in July 2015, with the launch of the Ethereum network and the issuance of its native crypto, Ether (ETH).
The Ethereum network is designed to enable the creation of decentralised applications (dApps) and smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
Ethereum’s initial coin offering (ICO) in 2014 raised over $18 million, and the platform has since grown to become one of the largest and most widely used blockchain platforms in the world. As of Jan 2023, Ethereum is valued at over $ 171 billion and is trading at $1543 ( market capitalisation and price is dynamic).
Ethereum has levelled up after the introduction of its newest upgrade known as the Merge. We will dive deeper into Ethereum Merge later.
How does Ethereum Differ from Bitcoin?

Purpose
Bitcoin was created primarily as a digital currency, while Ethereum was developed to build smart contracts and decentralised applications (dApps).

Blockchain technology
Both Bitcoin and Ethereum use blockchain technology, but Ethereum’s blockchain is more versatile and can support a wider range of applications.

Token
The token used on the Bitcoin network is Bitcoin (BTC), while the token used on the Ethereum network is Ether (ETH).

Supply
Bitcoin has a capped supply of 21 million coins, while the supply of Ether is not capped and will continue to be created through a process called staking.

Transaction speed
Bitcoin’s block time is around 10 minutes, while Ethereum’s block time is around 15 seconds, making Ethereum faster when it comes to confirmations of transactions.

Consensus algorithm
Ethereum and Bitcoin use different consensus algorithms. Ethereum uses Proof of Stake (PoS) and Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (PoW).

Flexibility
Ethereum’s flexibility allows for more complex and customizable decentralised applications to be built on top of it, whereas Bitcoin is primarily used as a digital currency.
Subscribe to get updated with Ethereum world
How Does Ethereum Work?
The Ethereum blockchain is a decentralised, and open-source platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralised applications (dApps). It uses a virtual machine, called the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), to execute the code of these smart contracts and dApps.
The Ethereum network is powered by Ether (ETH), the crypto used to pay for transactions and computational services on the network. Ethereum usage is through a consensus algorithm called Proof of Stake (PoS) which is different from Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm. In PoS, instead of miners solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain, validators are chosen based on the amount of Ether they hold and are willing to “stake” or lock up as collateral. The validators then earn the right to validate transactions and create new blocks in proportion to their stake.

What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine(EVM)?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the software environment that runs smart contracts and decentralised applications (dApps) on the Ethereum blockchain. It is a virtual machine that executes the code of these contracts and applications in a decentralised, trustless manner.
The EVM is responsible for enforcing the rules and executing the instructions of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It acts as a sandbox, isolating each contract from the rest of the network, ensuring that each contract can only access its data and the resources it is entitled to.
It’s important to note that the EVM is not a physical machine, but a software environment that runs on the computers of the Ethereum network’s nodes. Every node on the Ethereum network has a full copy of the EVM and can execute smart contracts and validate transactions. This makes the EVM a fundamental component of the Ethereum network, enabling it to be a decentralised, trustless platform for executing smart contracts and building decentralised applications.
What are Smart contracts?
Smart contracts on Ethereum are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts allow for the automation of digital assets and can be used for a wide range of applications, such as supply chain management, voting systems, financial transactions and much more.
What are dApps?
Decentralised applications (dApps) are built on top of the Ethereum blockchain, using the smart contract functionality to create applications that are not controlled by any single entity. The benefit of dApps is that they are open-source, transparent, and resistant to censorship and fraud.
Overall, Ethereum aims to provide a decentralised, global computer infrastructure that allows for the creation of new, and innovative applications, enabling developers to build online products without the need for centralized servers or intermediaries.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum’s long-awaited upgrade known as the “ Merge” is finally here. This upgrade is one of the most landmark events in the Ethereum ecosystem since of birth of Ethereum.
The primary difference between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0 is the consensus mechanism. Ethereum 2.0 works on a Proof of Stake(POS) consensus mechanism. Ethereum 1.0 operated on “Proof of Work”. As described earlier, Proof of Stake(POS) involves a validator staking their assets to validate transactions and earn rewards in Ether.
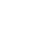
Ethereum’s first steps towards “the Merge” started in December 2020. This is when the project started running on two blockchains – the Mainnet which works on POW and the Beacon chain which works on POS. On September 15, 2022, the Beacon chain merged with the Mainnet thereby transitioning the entire blockchain to Proof of Stake which effectively reduced the energy consumption of the Ethereum blockchain by 99%.
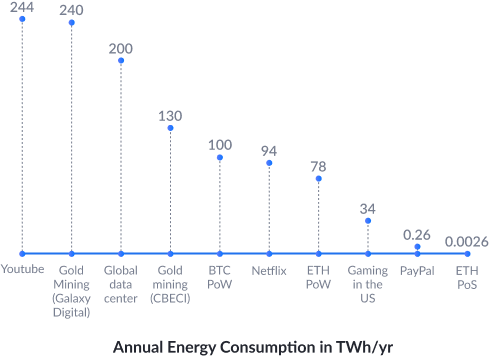
While the Merge was a landmark event, it is only the initial step in the elaborate “Ethereum Development Roadmap”. The next upgrades are
Each upgrade is set to solve critical roadblocks in the Ethereum blockchain, thereby making it more robust and universal.
The Ethereum Community and Ecosystem
What is the Vision of Ethereum?
Ethereum is one of the most robust crypto assets in the market today. While smart contract technology can be utilised across any field, there are a few specific problems which the Ethereum blockchain intends to address. Some of these are listed below.
Banking for everyone
Ethereum allows the underbanked and unbanked population of the world to be part of the global financial system. Traditional banking services are limited to a few whose borrowing criteria are linked to their credit score. Meanwhile, Ethereum can be accessed by anyone who has an internet connection.
To build a more private internet
Users who use applications hosted on the Ethereum blockchain don’t have to disclose all their personal information. Ethereum aims to build Web 3.0 which is based on value and not surveillance.
Peer-to-peer transactions
Users of the Ethereum blockchain do not need to deal with an intermediary to perform transactions. The blockchain acts as the medium between users.
Censorship Proof technology
Ethereum cannot be controlled by governments. The idea of a blockchain is itself resistant to censorship since it is based on a network of nodes that operate based on the blockchain rules.
Ethereum Applications
Defi
Decentralised finance(Defi) refers to financial systems and applications that are built on blockchain technology and are not controlled by any centralised authority. These systems are designed to be open, transparent, and accessible to anyone with an internet connection. The most common types of Defi applications include decentralised exchanges(DEXs), and lending and borrowing platforms.
One of the key advantages of Defi is that it allows for greater financial inclusion, as it enables individuals and organisations that may not have access to traditional financial services to participate in the global financial market.

NFTs
An NFT, or a non-fungible token, is a unique digital asset that can represent ownership of something digital, like digital art, music, video, virtual real estate, gaming items and much more. It is a certificate of ownership that proves that you own the NFT. The proof of ownership resides on the blockchain which makes the information immutable and indestructible.
Supply chain management
Ethereum can be used in supply chain management by creating smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. These smart contracts can be used to automate and track various aspects of the supply chain process, such as tracking the movement of goods, verifying product authenticity, and managing the transfer of ownership and payments. This can increase transparency and trust in the supply chain, as well as reduce the need for intermediaries and manual processes.

How to Stake Ethereum?
Ethereum staking is the process where Ethereum holders lock up a certain amount of Ether(ETH) to participate in the validation process of transactions on the blockchain.
When you stake your ETH, you become a validator on the Ethereum network. As a validator, you will be responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks on the Ethereum blockchain. In return for staking and performing this work, validators receive rewards in the form of newly minted ETH.
How to Buy Ethereum?
Ethereum can be bought on Centralised and Decentralised crypto exchanges.
ZebPay is one of the best Centralised exchanges to trade Ethereum. ZebPay only partners with platforms that are over-collateralised and assure the safety of our members’ assets. Additionally, ZebPay’s systems and processes are regularly audited to minimise investor risk. Our Information Security Management System is ISO-certified and stringent security protocols are in place to protect your data and assets. You can create an account on ZebPay and begin trading Ether today.
If you are ready to trade Ethereum using ZebPay, here is what you need to do.

Create a Free Account on ZebPay 
Users who want to Buy Bitcoin should create an account on ZebPay and verify their identity. The registration is free of charge.
- Register using the Zebpay App or Website
- Ensure that you use your valid email address and phone number during registration

Deposit Fiat Currency In Your ZebPay Wallet 
Before you buy BTC on Zebpay ensure that you have a minimum balance of INR 100 in your Zebpay wallet.
Deposits can be made using
 Bank Transfer
Bank Transfer

Buy Ethereum Through ZebPay App 
- Click on the Ethereum (ETH) icon in the Quick trade or Exchange panel
- Enter the INR amount you would like to invest
- The quantity of Ethereum that you can purchase will be displayed
- Check all the order details
- Click on Place Buy Order
- Voila! Your order is placed
Buy Ethereum Through ZebPay Website 
- Login to Zebpay on your desktop web browser
- Click on Quick Trade or Exchange based on your preference
- Enter the INR amount you want to invest
- Preview your order and check all the order details
- Place your order
Is Ethereum Decentralised?
Ethereum is a fully decentralised crypto. It is not owned by a single entity. The Ethereum blockchain is run by a network of nodes. All transactions in Ethereum are recorded on the blockchain which makes the system transparent, foolproof and secure.
Future of Ethereum
Ethereum has significant potential due to its smart contract functionality and its status as the second-largest crypto by market capitalization. Some believe that Ethereum has the potential to become the dominant blockchain platform for decentralised applications and that its value will continue to rise in the future. But the future of Ethereum has three focus areas that are being addressed.
Scalability
Future upgrades of Ethereum aim to process 1000s of transactions per second. This will make the blockchain more suitable for the development of applications for the masses.

Security
The next set of upgrades addresses the security of the blockchain. Ethereum already has robust security measures but the aim is to ramp it up and take it to a level never seen before.

Sustainability
The Merge has already reduced the energy consumption of the blockchain by close to 99%. This is a landmark step in making Ethereum sustainable.
Limitations of Ethereum
Ethereum, like any other blockchain, has certain limitations that could affect its scalability, and performance. Some of the main limitations of Ethereum include

Complexity
Ethereum is a complex system that requires a high level of technical knowledge to understand and use. This can be a barrier for some individuals and businesses.

Immutability
The immutability of the blockchain could cause problems in case of errors or malicious intent on smart contracts, the only way to fix it is through a hard fork which is a complex and risky process.

Regulations
Ethereum is a decentralised and open platform, but regulations vary from one country to another, this could be a barrier for some use cases or the adoption of the platform.
These limitations are being addressed by Ethereum’s development team and the community, through various initiatives such as Ethereum 2.0 and upcoming scaling solutions such as sharding.
Is Ethereum a Good Investment?
Ethereum is one of the most robust assets in the crypto market today and it will continue to be one because of its vision, and the real-world problems that it solves. Since its inception, Ethereum has surpassed all tokens other than Bitcoin in terms of market capitalisation. This shows the level of acceptance of Ethereum all over the world. It is a fundamentally rock-solid asset and it might soon change the way we interact with the internet.