Smart contracts are one of the most promising innovations in blockchain technology. By adding conditional logic (if X happens, then do Y) onto blockchain’s distributed ledger, we can create contracts that cannot be tampered with.
One way to use this technology? Bringing crop insurance to farmers in India.
Chainlink has published a paper in collaboration with the World Economic Forum laying out a new standard for integrating traditional infrastructure with blockchain technology.
The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
The scheme was launched in 2016 to give farmers insurance to protect them against crop failure. In addition to providing a safety net to the country’s farmers, the scheme hopes to encourage them to modernize their practice.
Most of the insurance premium is covered by the central and state governments, while the farmer pays a maximum of 2% annually.
As a result, the large scale of the programme is evident, as reported in the Kharif season (June–October) of 2019.
- Total farmers covered – 18 million
- Crop area insured – 23 million hectares
- Total premium – $2 billion
In order to implement this scheme, many external stakeholders need to join hands. Now, when each of these stakeholders use technical systems to collect and process data, it becomes difficult to coordinate and share information.
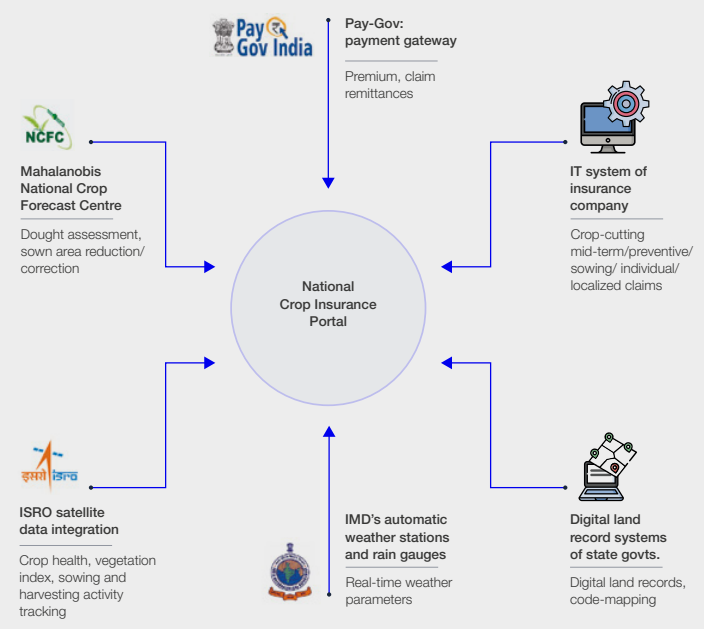
How will Chainlink help?
Chainlink can help these different agencies coordinate using oracle programs. An oracle can connect a blockchain-based contract with real-world data – helping systems speak to one another. The paper recommends that agencies use decentralized networks of oracles, to guarantee the data’s accuracy, and its security.
This brings the following benefits:
Transparency and accountability
Transactions on the blockchain cannot be altered, and are completely transparent. As a result, this network can serve as a trustworthy common data store for participants, by sharing blockchain nodes with all stakeholders,.
Reducing corrupt behaviour
Smart contracts can be programmed to automatically transfer welfare benefits to farmers directly. Consequently, there is no human discretion in settling claims.
Information security
While keeping information secure only through traditional methods may not be very effective, employing a blockchain makes it difficult to break in and alter records.







