Most people associate blockchain primarily with Bitcoin, but the technology extends far beyond powering a single crypto asset. At its core, blockchain is a decentralised, transparent, and secure system that enables trustless interactions, which refer to features that have unlocked innovation across multiple industries, from finance and gaming to supply chains and digital identity.
One of the most impactful applications of blockchain technology is the rise of decentralised applications (dApps). Unlike traditional apps that rely on central servers, dApps run on blockchain networks, offering greater transparency, enhanced security, and improved user control over data and assets. These benefits have driven rapid adoption and experimentation across the crypto ecosystem.
In this article, we explore some of the top decentralised applications (dApps) available today, highlighting how they work, what makes them unique, and why they are gaining popularity in the evolving blockchain landscape.
Also Read: Top 10 Layer-1 Blockchain Cryptos in 2026
An Introduction to Decentralised Applications (dApps)
A dApp, or decentralised application, functions much like any other app you use on your smartphone, but with one key difference: it is built on blockchain technology, which adds powerful layers of security, transparency, and user control. Instead of relying on central servers, dApps leverage the blockchain to deliver features that traditional applications cannot.
One of the biggest advantages of decentralised applications is privacy and ownership of data. In a dApp ecosystem, users retain control over their information, and data cannot be accessed, altered, or monetised by a central company or third party. This shift empowers users by removing intermediaries and reducing the risk of data misuse.
Unlike conventional apps controlled by a single organisation, a dApp runs on a distributed network of nodes. These nodes, referred to as computing devices operated by users around the world, store and validate copies of the blockchain. As a result, the application is maintained and governed collectively by its network, rather than by large tech companies such as Meta or Google.
DApps exist across a wide range of use cases, including gaming, social media, and decentralised finance (DeFi). What unites them is their use of smart contracts, which’re self-executing programs on the blockchain that automate rules, transactions, and governance. By combining smart contracts with decentralised networks, dApps are redefining how applications are built, managed, and used in the digital age.
Also Read: 10 Best Cryptos to Buy Under $1 in 2026
Top 10 Popular dApp Tokens
Here is a list of dApp tokens trending right now:
| Token Name | Current Price | Market Capitalization | 24-Hour Volume |
| Arbitrum (ARB) | $0.1150 | $670.52 million | $66.01 million |
| Kite (KITE) | $0.2051 | $369.26 million | $125.20 million |
| Starknet (STRK) | $0.04928 | $267.48 million | $28.81 million |
| Meteora (MET) | $0.2220 | $111.05 million | $11.74 million |
| SoSoValue (SOSO) | $0.3897 | $106.84 million | $2.27 million |
| Yooldo (ESPORTS) | $0.3497 | $95.07 million | $137.12 million |
| Magic Eden (ME) | $0.1357 | $62.61 million | $27.15 million |
| Astar (ASTR) | $0.007938 | $67.83 million | $1.91 million |
| aelf (ELF) | $0.08099 | $66.74 million | $1.59 million |
| TronBank (TBK) | $0.3403 | $54.16 million | $344.40K |
Arbitrum (ARB)
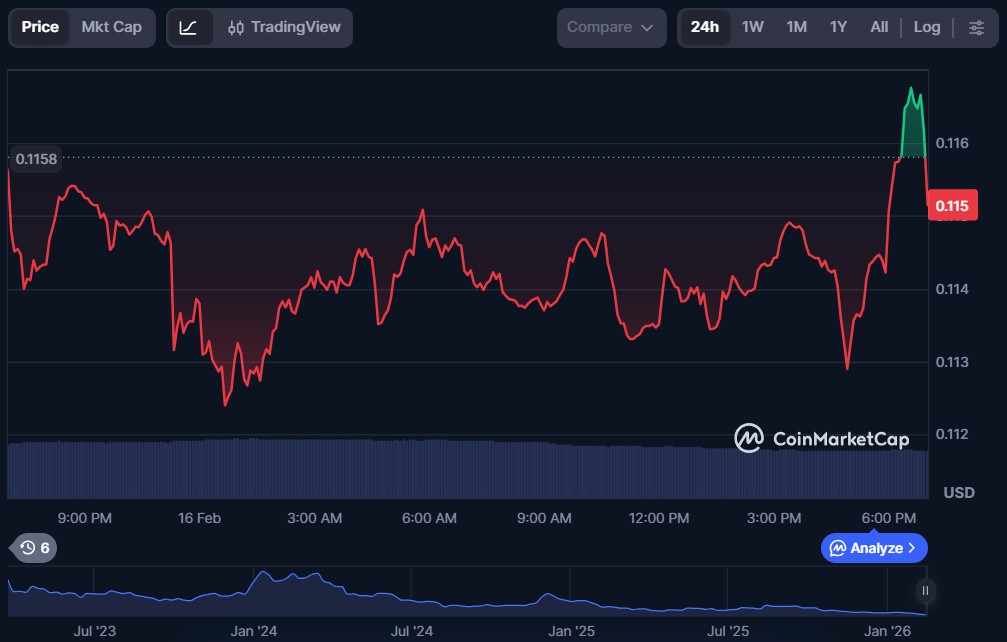
Arbitrum is a decentralised Layer-2 scaling solution built on top of the Ethereum blockchain that aims to improve transaction speed and reduce gas costs for users and developers. It leverages smart contracts to enable faster and more efficient Ethereum activity, making it easier to build and interact with decentralised applications. The ecosystem also supports a growing number of DeFi protocols, NFTs, and other on-chain services that benefit from lower fees and higher throughput.
ARB is the platform’s native governance token. Holders can participate in decision-making through the Arbitrum DAO and influence upgrades, treasury allocation, and ecosystem incentives.
Kite (KITE)
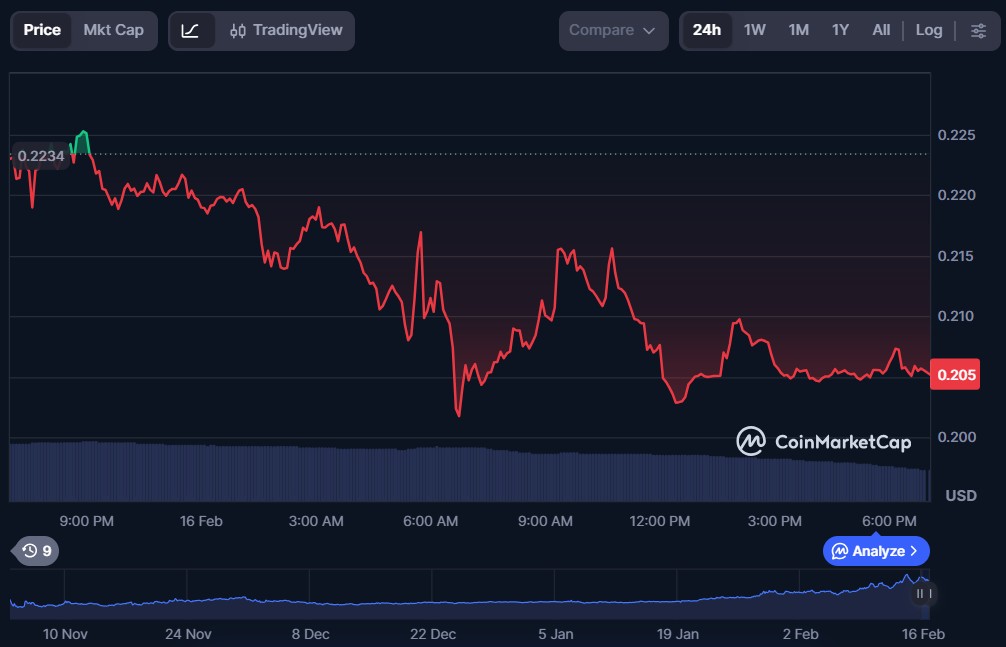
Kite is a decentralised blockchain project that operates on an EVM-compatible Layer-1 network designed for autonomous AI-powered agent interactions. It uses smart contracts to enable fast, low-cost transactions and on-chain identity and governance for AI applications, opening up new possibilities for digital payments and programmable workflows. The platform’s modular ecosystem supports developers building autonomous services that interact seamlessly with the network.
KITE is the native token of the Kite blockchain. It supports network incentives, governance participation, and ecosystem engagement, with plans to expand its utility as the protocol evolves.
Starknet (STRK)
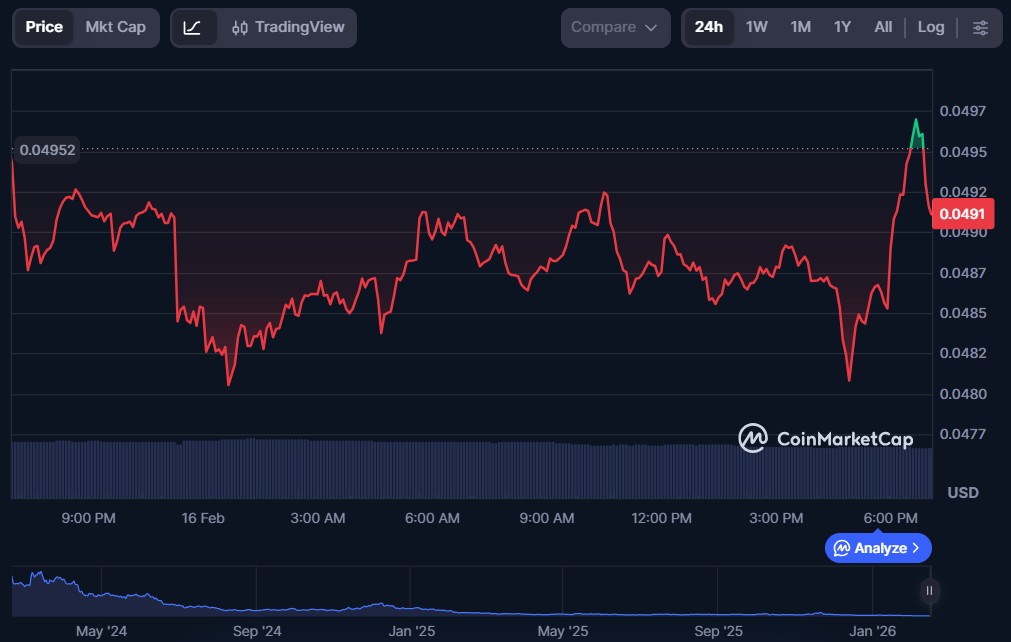
Starknet is a decentralised Ethereum scaling protocol that uses zero-knowledge proofs (zk-rollups) to increase transaction throughput while maintaining high security and low fees. The smart contracts on Starknet enable a wide range of applications, from DeFi to NFTs, with improved scalability compared to Ethereum mainnet execution. Its architecture helps developers launch more efficient dApps without compromising on decentralisation.
STRK is the protocol’s native token. It is used for governance and can be staked to support network security and participate in decision-making processes within the Starknet ecosystem.
Meteora (MET)
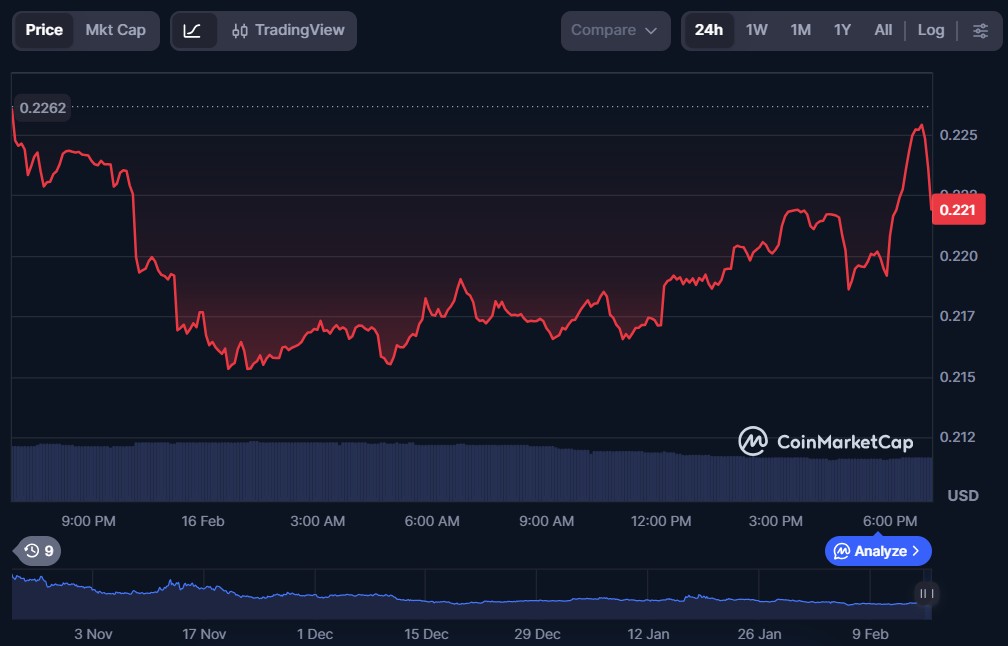
Meteora is a decentralised liquidity protocol built on the Solana blockchain that focuses on improving how liquidity is provided and managed across DeFi applications. It employs smart contracts and novel liquidity-optimization tools like dynamic liquidity market makers to reduce slippage and enhance capital efficiency for traders and liquidity providers. The platform also supports fair token launches and yield-generating opportunities.
MET is Meteora’s native token. It offers governance rights, staking incentives, and rewards for liquidity participation, helping drive growth within the Solana DeFi ecosystem.
SoSoValue (SOSO)
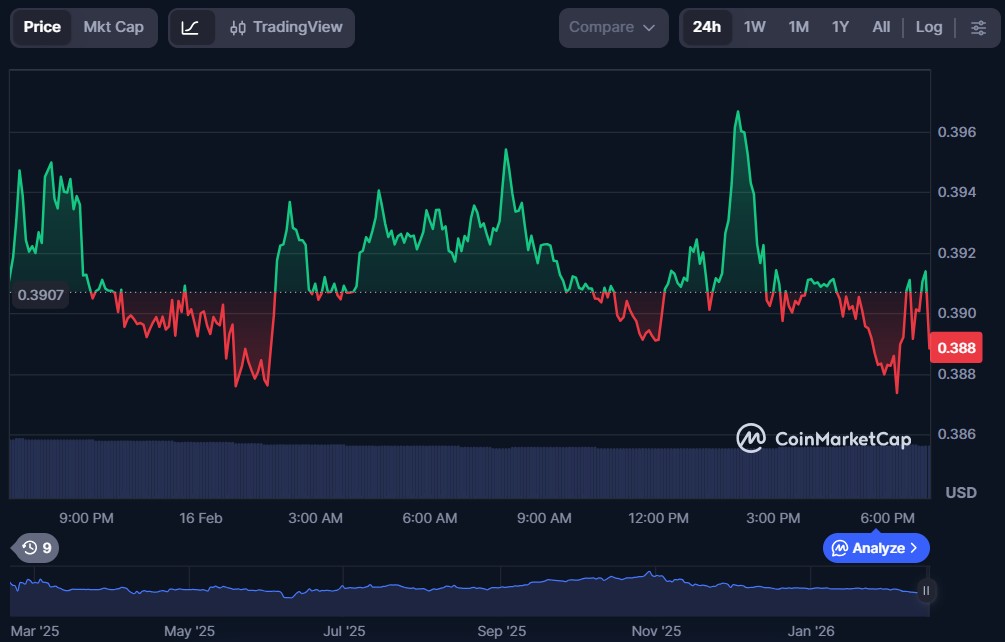
SoSoValue is a decentralised token integrated with blockchain-based applications designed to deliver value through community-driven engagement and utility-centric features. The ecosystem often rewards active participants and token holders by enabling them to interact with various DeFi functions, loyalty incentives, and potential staking or reward mechanisms that foster long-term involvement.
SOSO serves as the native token for the SoSoValue platform, granting holders access to governance cues, ecosystem incentives, and potential participation in network-related reward programs that support community growth.
Also Read: Top 5 Cryptos by Market Capitalization
Yooldo (ESPORTS)
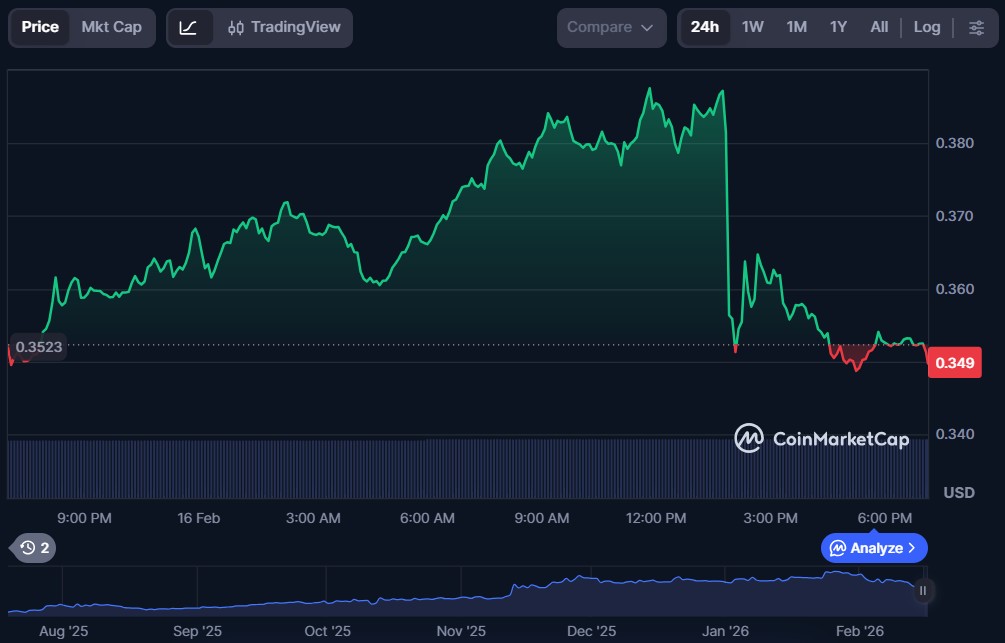
Yooldo (ESPORTS) is a blockchain-enabled gaming and esports platform that integrates decentralised elements such as on-chain rewards, token incentives, and staking features for competitive gamers and community members. By using smart contracts, the platform facilitates transparent reward distribution, tournament mechanics, and play-to-earn experiences that leverage the wider Web3 gaming ecosystem.
ESPORTS is the native token of Yooldo. It is used for participant rewards, incentive structures, and engagement programs within the platform, aiming to align interests between players and the broader community.
Magic Eden (ME)
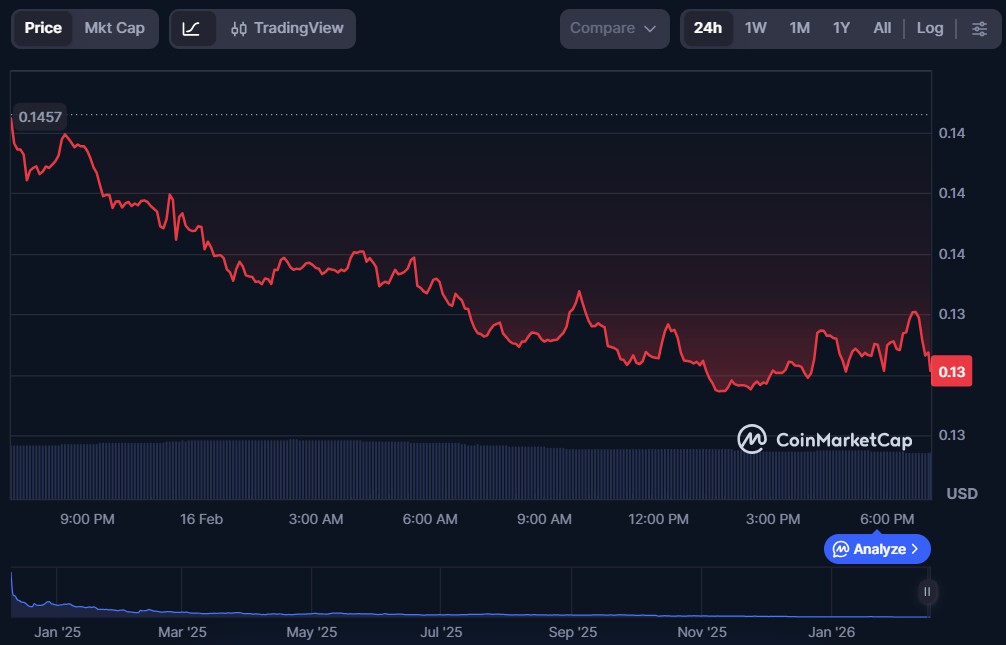
Magic Eden is a decentralised marketplace and ecosystem focused on NFTs, enabling users to discover, trade, and mint digital assets across multiple blockchain networks. It relies on smart contracts to facilitate secure, peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, bringing creators and collectors together in a permissionless environment.
ME is Magic Eden’s native token. It rewards platform participation, supports governance decisions, and can provide benefits to users engaged in the ecosystem’s growth and development.
Astar (ASTR)
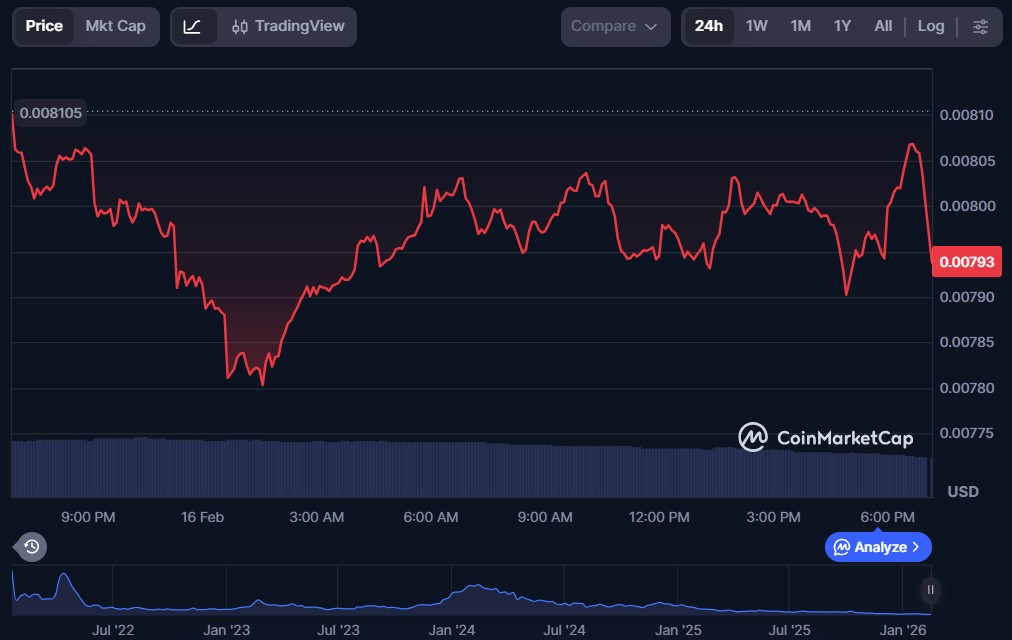
Astar is a multi-chain smart contract platform that enables dApps to run across multiple Layer-1 and Layer-2 networks, giving developers flexibility and interoperability. By using its underlying blockchain infrastructure, Astar supports a wide range of applications, including DeFi, NFT projects, and Web3 innovations that require cross-chain connectivity.
ASTR is the native token of the Astar ecosystem. It enables staking rewards, governance participation, and contributions to network security and resource allocation across connected chains.
aelf (ELF)
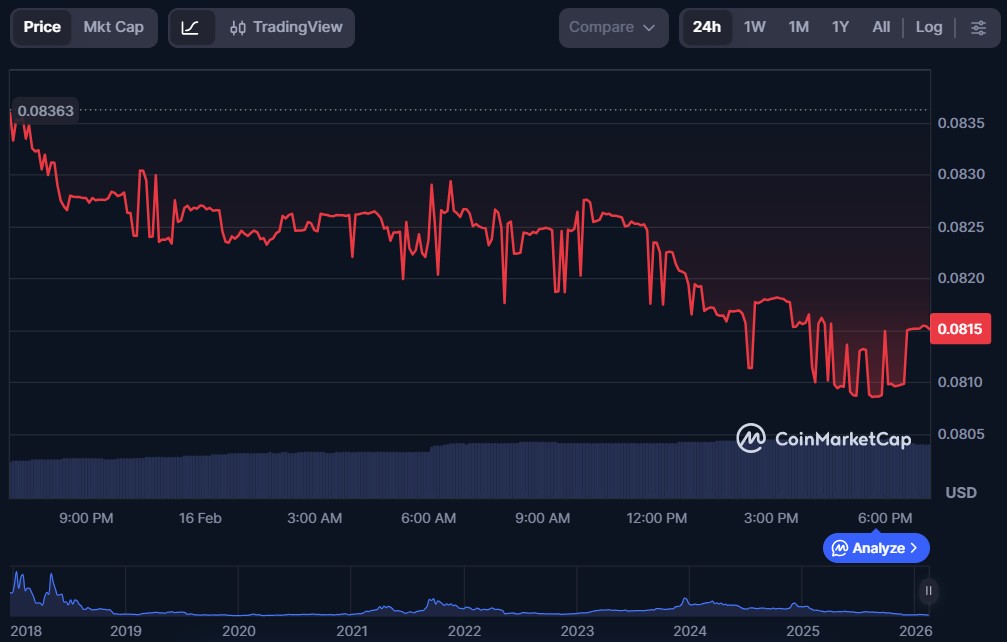
Aelf is a decentralised cloud computing blockchain network designed to support high-performance smart contracts and enterprise-grade dApps. Its modular architecture allows parallel processing and scalable infrastructure, enabling efficient transaction settlement and flexible deployment for developers building on its platform.
ELF is the native utility and governance token of the network. It helps secure the ecosystem, supports staking rewards, and allows token holders to participate in governance decisions on protocol upgrades and funding directions.
Also Read: USDT vs. USDC
TronBank (TBK)
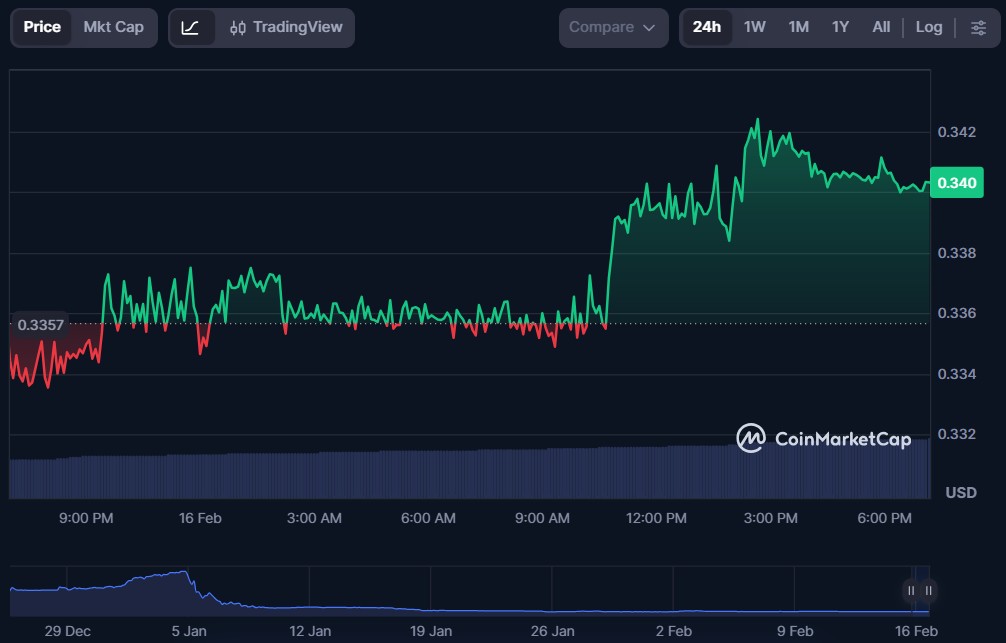
TronBank (TBK) is a decentralised finance protocol operating within the broader blockchain ecosystem, offering financial services such as lending, borrowing, and yield opportunities through smart contracts. By leveraging decentralised infrastructure, the platform aims to deliver transparent and permissionless financial products to users without central intermediaries.
TBK is the native token of TronBank’s protocol. It plays a role in incentive programs, governance participation, and access to exclusive platform features, helping align user incentives with ecosystem growth.
Also Read: MP Raghav Chadha Voices Support for Crypto
Conclusion
Decentralised applications are transforming the digital landscape by leveraging blockchain technology to offer greater transparency, security, and user control without relying on central intermediaries. From DeFi platforms and NFT marketplaces to gaming and scalability solutions, dApps showcase how smart contracts and decentralised networks are enabling new ways to build and use applications. As this ecosystem continues to grow, understanding how dApps function and the role of their native tokens can help users better navigate the evolving Web3 space and make more informed decisions.
In the grand scheme of things, ZebPay blogs are here to provide you with crypto wisdom. Get started today and join 6 million+ registered users to explore endless features on ZebPay!
FAQs on Decentralised Applications (dApps)
What are decentralised applications (dApps)?
Decentralised applications, or dApps, are applications built on blockchain networks that operate without a central authority. They use smart contracts to function autonomously and allow users to interact directly with the platform in a transparent and permissionless manner.
How are dApps different from traditional applications?
Unlike traditional apps that are controlled by a single company and run on central servers, dApps operate on distributed blockchain networks. This means users retain greater control over their data, and the application’s rules are enforced by code rather than a central organisation.
What role do smart contracts play in dApps?
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain that automate processes such as transactions, governance, and rewards. They ensure that dApps function securely and transparently without manual intervention or intermediaries.
What types of dApps exist today?
DApps span a wide range of use cases, including decentralised finance (DeFi), NFT marketplaces, gaming, social platforms, and infrastructure solutions. Each category uses blockchain technology to offer features that are not easily achievable with traditional applications.
Do I need a crypto asset to use dApps?
Most dApps require users to hold crypto to pay network fees and interact with smart contracts. Depending on the blockchain, this could involve tokens such as ETH, BNB, or others used for transactions and platform-specific activities.
Are dApps safe to use?
While dApps offer strong security through blockchain technology, they are only as safe as the smart contracts they rely on. Users should always research the platform, understand the risks, and follow best practices such as using trusted wallets and verified applications.






